Raw food diet: A comprehensive guide to a healthy and natural lifestyle

Raw Food Diet: A Pathway to Health and Well-Being
Introduction:

The concept of a raw food diet has gained significant popularity in recent years, as more and more individuals seek ways to improve their health and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of the raw food diet, including its definition, various types, quantitative measurements, differences between approaches, and a historical overview of its advantages and disadvantages. By delving into these aspects, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of this dietary lifestyle and its potential benefits for individuals looking to embrace a more natural and nourishing approach to food.
A Comprehensive Overview of the Raw Food Diet
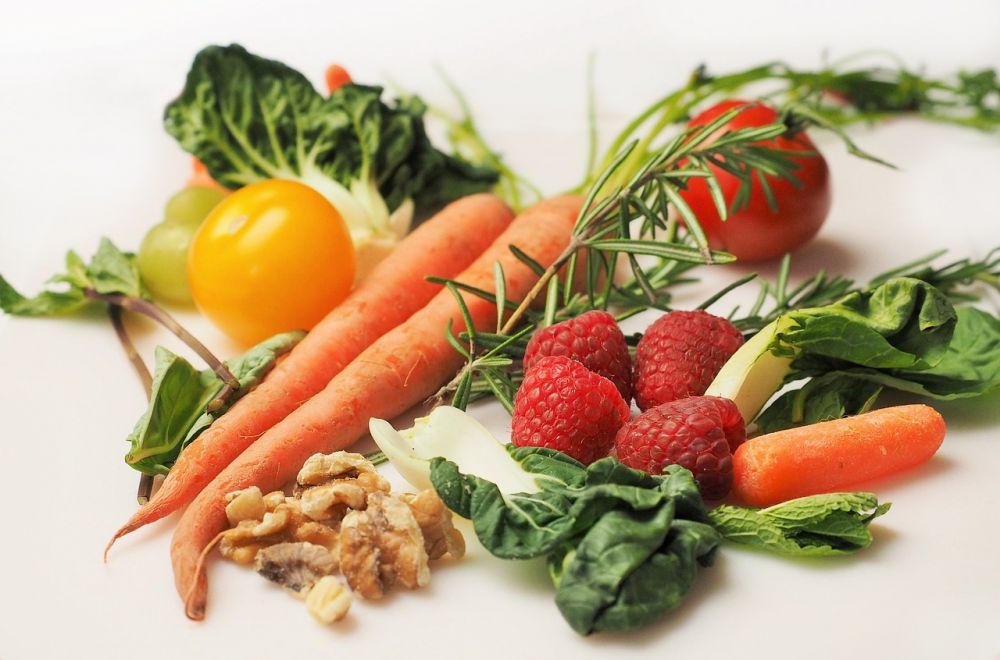
The raw food diet, also known as raw veganism or living food cuisine, is an organic and unprocessed approach to nutrition that primarily consists of consuming plant-based foods in their natural, uncooked state. Advocates of this diet believe that cooking destroys essential enzymes and nutrients present in food, and that consuming uncooked foods preserves these vital components, resulting in improved health and vitality. While the raw food diet emphasizes the consumption of raw fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, there are variations within the diet that allow for some processed or lightly cooked foods.
Exploring Different Types of Raw Food Diets
1. Raw Vegan Diet:
The raw vegan diet forms the core of the raw food dieting philosophy. It involves the consumption of unprocessed fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouted grains. This type of raw food diet excludes all animal products, including dairy and honey.
2. Raw Vegetarian Diet:
Similar to the raw vegan diet, the raw vegetarian diet includes uncooked plant-based foods. However, it allows for the consumption of certain animal products, such as raw eggs, unpasteurized dairy, and honey.
3. Raw Omnivorous Diet:
The raw omnivorous diet follows the principles of the raw food diet but allows for the inclusion of raw animal products, such as raw fish, raw meat, and raw milk.
4. Raw Paleo Diet:
The raw paleo diet combines aspects of the raw food diet with the paleo diet, which is based on consuming foods that our ancestors would have eaten. This type of raw food diet emphasizes the consumption of raw meat, fish, eggs, and non-starchy vegetables, while excluding grains, legumes, and processed foods.
Quantitative Measurements on the Raw Food Diet
Proponents of the raw food diet believe that consuming a primarily raw diet provides numerous health benefits. However, it is essential to analyze quantitative measurements to understand the potential impact on nutrient intake. Research suggests that individuals following a raw food diet may have lower intakes of certain nutrients, such as calcium, vitamin D, iron, and vitamin B12. However, they tend to have higher intakes of antioxidants, fiber, and other essential vitamins and minerals.
Understanding the Differences between Raw Food Diet Approaches
Although the core principle of the raw food diet remains the same across the different variations, there are notable differences in its implementation. Some individuals prefer a 100% raw diet, while others incorporate a percentage of cooked or processed foods. These variations allow for a more flexible approach and can be modified based on individual preferences, lifestyle, and nutritional needs.
Historical Overview of the Pros and Cons of Raw Food Diets
Raw food diets have been practiced throughout history by different cultures, including ancient civilizations. While the consumption of raw foods provides various advantages, such as increased nutrient intake, improved digestion, and weight management, it is not without its drawbacks. Historically, concerns have been raised regarding the risk of bacterial or parasitic infections due to uncooked animal products and the potential difficulty in meeting certain nutritional requirements.
Conclusion:
The raw food diet offers a holistic approach to nutrition, focusing on the consumption of uncooked and natural plant-based foods. By understanding its various types, quantitative measurements, differences between approaches, and historical advantages and disadvantages, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating elements of the raw food diet into their lifestyle. While it is essential to consider individual nutritional requirements and potential limitations, embracing a raw food diet may offer significant benefits toward achieving enhanced health and well-being for those seeking a more natural and nourishing dietary approach.